Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs: A Comprehensive Guide
Dec 10, 2025
Content
Generators are essential tools for providing backup power, ensuring uninterrupted operations, and powering equipment in remote locations. Whether you are considering a generator for home use, industrial applications, or recreational activities, selecting the right one can be a daunting task. There are various types of generators available, each offering different features and capabilities. The key to making the right choice lies in understanding your specific power needs and the factors that affect generator performance.
Understand Your Power Requirements
The first and most important step in choosing a generator is understanding your power needs. A generator is rated by its wattage output, which indicates the amount of electrical power it can produce. To determine the size of the generator you need, make a list of the equipment or appliances you intend to power, along with their power ratings.
Calculating Power Demand
For home use, typical appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting each require a specific amount of power. For example:
A refrigerator may require 600 to 800 watts.
Air conditioners can require 2000 to 4000 watts, depending on the size.
Lights typically require 60 to 100 watts per bulb.
By adding up the wattage of all the appliances you plan to run at the same time, you can estimate the total wattage you’ll need from your generator. It’s important to account for both running watts (the continuous power needed to run equipment) and surge watts (the extra power required to start equipment, like motors in refrigerators or air conditioners).
Consider Future Needs
When calculating your power requirements, be sure to consider any future additions. If you plan to add more equipment, tools, or appliances in the future, it’s wise to choose a generator with a higher wattage rating than your current needs. This will ensure you don’t outgrow your generator too quickly.
Types of Generators
Generators come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Understanding the differences between these types can help you make an informed choice.
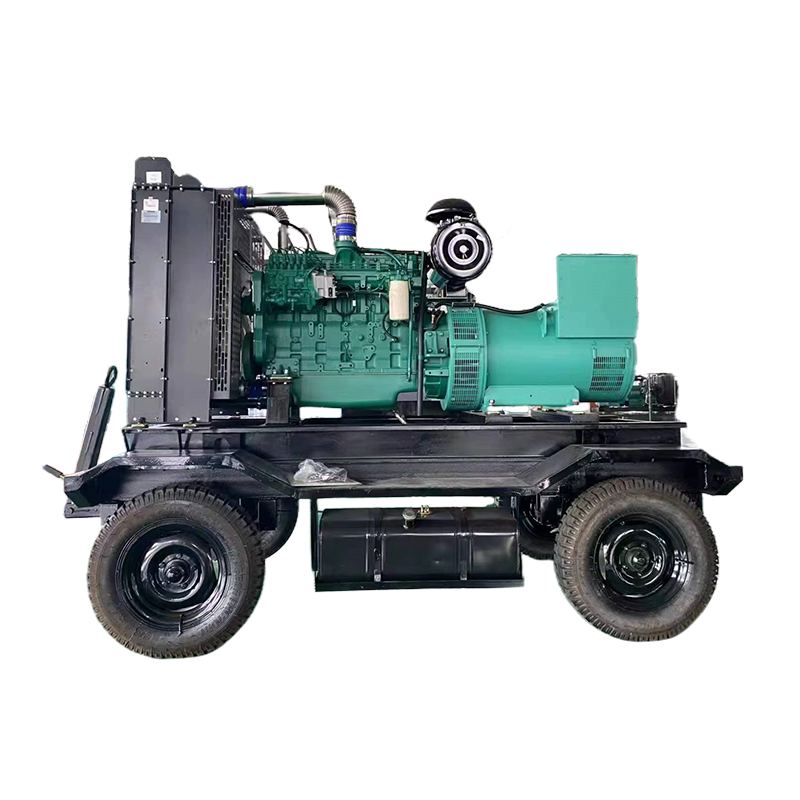
Portable Generators
Portable generators are versatile units designed for both residential and small business use. They can provide backup power during outages or power tools and equipment at remote job sites. These generators typically run on gasoline, diesel, or propane and offer a range of power outputs.
Best for: Homeowners, outdoor enthusiasts, and small businesses.
Power Range: 1,000 to 10,000 watts.
Advantages: Portability, ease of use, and a wide selection of sizes and prices.
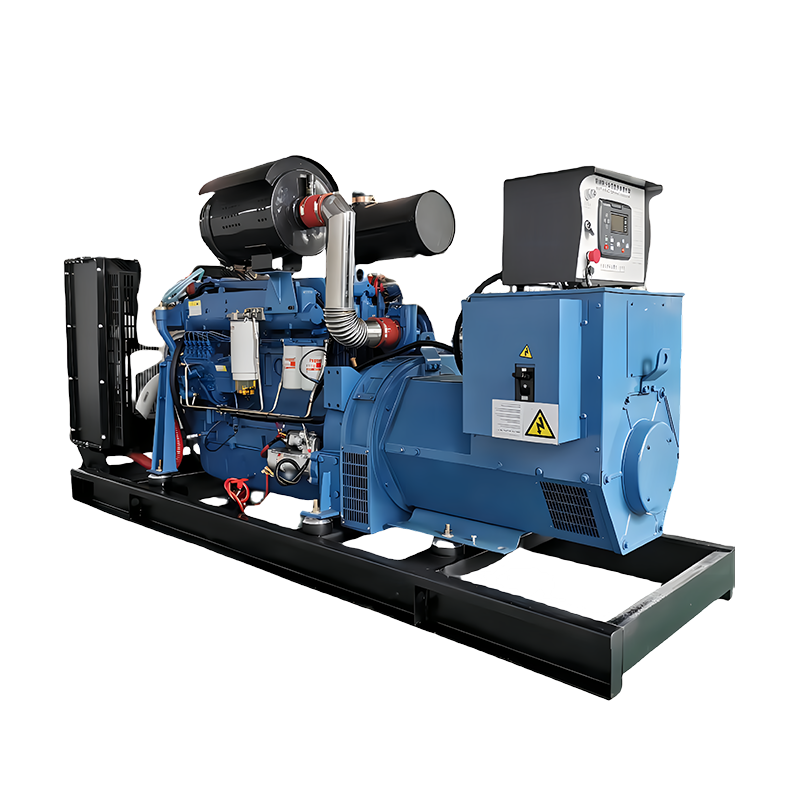
Standby Generators
Standby generators are permanently installed outside a home or business and are connected to the electrical system. These generators automatically turn on when there is a power outage, providing seamless backup power without the need for manual intervention.
Best for: Homeowners and businesses requiring uninterrupted power.
Power Range: 5,000 to 50,000 watts or more.
Advantages: Automatic startup, reliable power source, and the ability to power entire homes or commercial buildings.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are designed to produce cleaner, more stable power than conventional portable generators. They are ideal for powering sensitive electronics like computers, phones, and televisions. Inverter generators are also quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional models.
Best for: Small appliances, sensitive electronics, and recreational use.
Power Range: 1,000 to 4,000 watts.
Advantages: Quiet operation, compact size, and clean energy output.
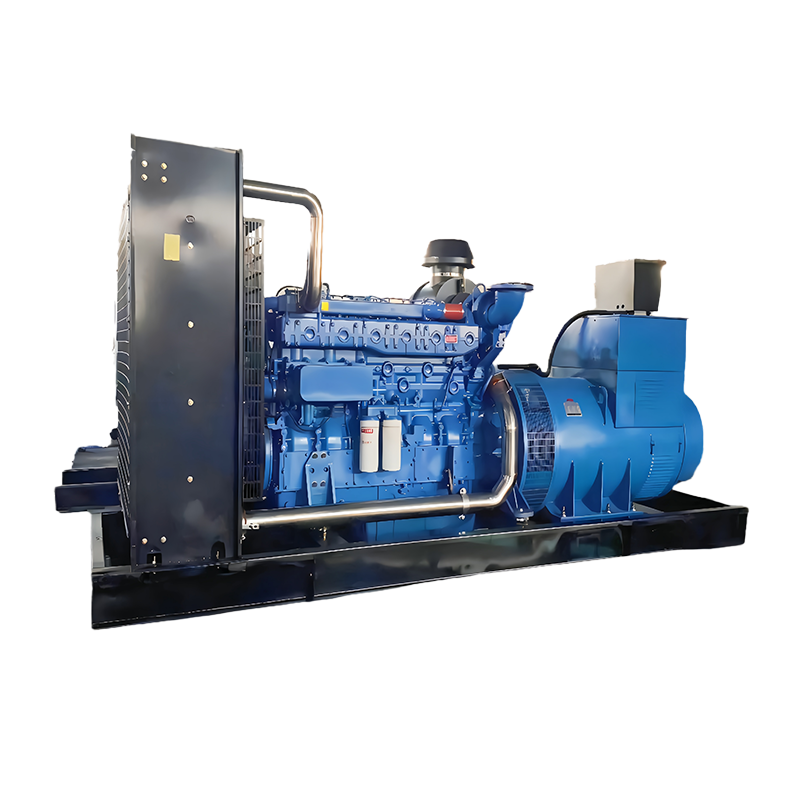
Industrial Generators
Industrial generators are large, heavy-duty units designed to supply power to factories, construction sites, or entire buildings. They typically run on diesel or natural gas and can handle high-demand power loads for extended periods.
Best for: Large-scale operations, construction projects, and industrial applications.
Power Range: 10,000 watts and up.
Advantages: High power output, long runtime, and durability.
Fuel Type Considerations
When choosing a generator, the type of fuel it uses is a significant consideration. Different fuel types come with their own advantages and drawbacks, depending on your specific needs.
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline is one of the most common fuel types for portable generators. Gasoline-powered units are widely available, and fuel is relatively inexpensive and easy to store. However, gasoline has a shorter shelf life, and gasoline-powered generators may be less fuel-efficient than other options.
Best for: Short-term backup power and occasional use.
Advantages: Easy to find fuel, cost-effective.
Drawbacks: Shorter shelf life, less efficient, noisy.
Diesel Generators
Diesel-powered generators are known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and long runtime. Diesel fuel is less flammable and has a longer shelf life compared to gasoline. These generators are often used in industrial settings or for long-term, high-power applications.
Best for: Industrial use, large-scale backup power.
Advantages: Fuel efficiency, long lifespan, and reliability.
Drawbacks: Noisier than gasoline models, higher initial cost.
Propane Generators
Propane generators are cleaner-burning and more environmentally friendly than gasoline or diesel models. Propane is also easy to store, and propane generators tend to have longer shelf lives compared to gasoline units. However, propane may not be as readily available in some areas.
Best for: Homeowners seeking a cleaner fuel option, remote locations with propane supply.
Advantages: Clean-burning, long shelf life, and availability of dual-fuel options (gasoline/propane).
Drawbacks: Propane availability may be limited in some areas.
Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas generators are typically used for permanent installations, especially in homes or businesses with access to natural gas lines. They offer continuous, clean power and are relatively low-cost to operate compared to gasoline or diesel models.
Best for: Homes and businesses with access to natural gas.
Advantages: Continuous power, lower operating costs, clean energy.
Drawbacks: Limited to areas with natural gas infrastructure.
Size and Portability
The size and portability of the generator are important factors to consider. For homeowners and small businesses, a portable generator may be sufficient, while larger operations might require a standby or industrial model.
Portability
If you need a generator for outdoor activities or to power tools at remote job sites, portability will be a key factor. Look for a generator with wheels, a compact design, and an ergonomic handle for easy movement.
Size
Consider both the physical size of the generator and its power output. Industrial generators are large and require ample space, while portable generators are designed to be more compact and easier to store.
Noise Level and Environmental Impact
Noise can be an issue with some generators, especially portable models. Noise levels are typically measured in decibels (dB), and generators can range from quiet (50–60 dB) to loud (80–90 dB). If you plan to use your generator in a residential area or near sensitive environments, look for models that are specifically designed to operate quietly.
Inverter generators are typically quieter than traditional portable generators and are ideal for locations where noise is a concern.
Maintenance and Warranty
Like any piece of equipment, generators require regular maintenance to ensure longevity and reliability. Choose a generator that offers easy maintenance, such as accessible air filters, oil changes, and spark plugs. Many manufacturers offer warranties, which can be crucial for ensuring peace of mind in case of malfunction.
Budget Considerations
Generators come in a wide range of prices, depending on their type, size, and features. It’s essential to balance your budget with your needs. While a high-end generator may offer more advanced features, it might be overkill if your power requirements are minimal. At the same time, opting for a lower-cost generator could result in sacrificing essential features, efficiency, or longevity.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى