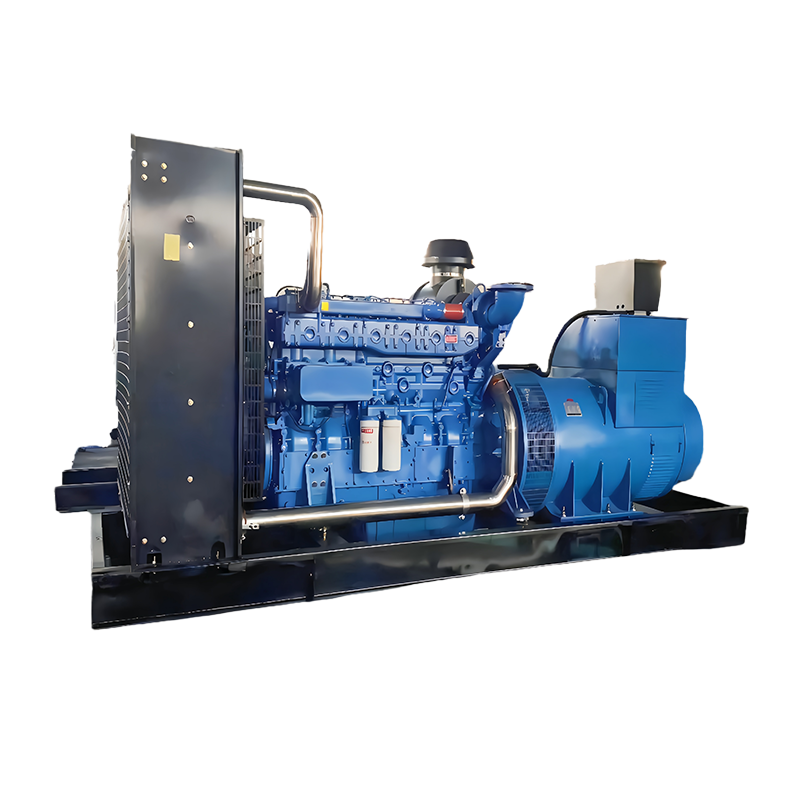
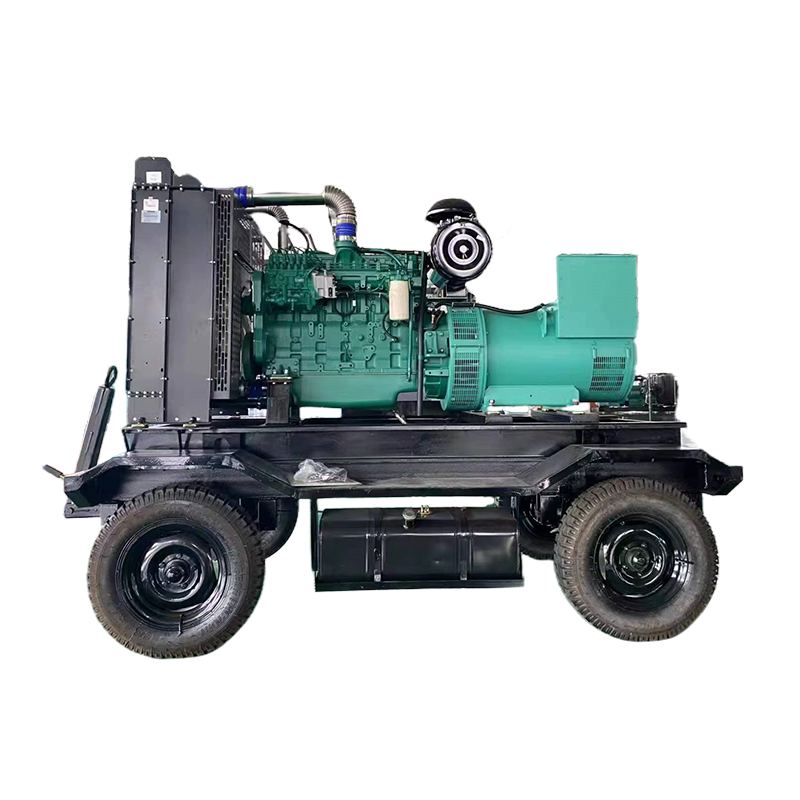
The Role of Diesel Generators in Ensuring Uninterrupted Power in Critical Infrastructure
Nov 12, 2025
Content
In today’s fast-paced world, reliable and continuous power supply is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. For critical infrastructure such as hospitals, data centers, transportation hubs, and telecommunications facilities, power interruptions can have severe consequences, ranging from financial losses to endangering human lives. While the power grid provides the primary source of electricity, it is susceptible to outages caused by severe weather, natural disasters, equipment failures, or even human error. This is where diesel generators play a crucial role.
Diesel generators have long been relied upon as an efficient and reliable backup power source, offering a fail-safe option to ensure that essential services continue to operate seamlessly, even during power disruptions.
Immediate Response to Power Failures
When a power outage occurs, critical infrastructure such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency response centers cannot afford even a second of downtime. In these situations, diesel generators serve as the first line of defense, stepping in almost immediately to take over the load from the main power grid.
Unlike other backup systems such as battery-powered UPS (uninterruptible power supply) units, which offer only limited runtime, diesel generators can run for extended periods, providing continuous power until the grid is restored or other power sources are available. The ability of diesel generators to kick in within seconds after a power failure is vital in ensuring there is no interruption in the services these critical sectors provide.
For instance, hospitals require constant power for life-saving equipment, including ventilators, heart monitors, and surgical tools. A diesel-powered backup is capable of keeping these systems running for as long as necessary, even during prolonged outages, ensuring patient safety is never compromised.
Reliability and Robustness
One of the key reasons diesel generators remain a popular choice for backup power is their reliability and robustness. Diesel engines are known for their ability to operate efficiently even under harsh conditions. Whether it's in extreme heat, cold, or in locations with high humidity, diesel generators are built to withstand and perform in the most challenging environments.
For critical infrastructure, where failure is simply not an option, the durability of a diesel generator ensures long-term dependability. These generators are designed to provide high power output over extended periods, making them ideal for facilities that require continuous operation, such as telecommunications hubs or airports.
In addition, diesel fuel is widely available and can be stored for long periods, offering greater self-sufficiency compared to other backup power sources like natural gas, which may depend on an external pipeline infrastructure that can be disrupted.
Meeting High Power Demands
Critical infrastructure facilities often have high and fluctuating power demands, which may change based on the time of day, workload, or operational needs. Diesel generators are uniquely suited for these applications because they can be scaled to meet varying power loads, from small office buildings to large industrial complexes.
Data centers, which house sensitive digital infrastructure, require enormous amounts of power to ensure smooth operations. These centers rely heavily on diesel generators to back up their operations in case of power failure. Diesel generators can supply the consistent, reliable power that these facilities need to prevent downtime, which can lead to data loss or even security breaches.
Similarly, in industries like manufacturing, where production lines depend on machinery that must run continuously, diesel generators ensure that operations continue smoothly without interruptions, protecting both profits and productivity.
Cost-Effectiveness
For many organizations, investing in diesel generators proves to be more cost-effective than relying solely on other backup power systems. While upfront costs for diesel generators may be higher than other alternatives, they are more affordable and cost-efficient to operate and maintain in the long term.
Diesel engines are known for their fuel efficiency, and when maintained properly, they can provide years of reliable service. The relatively low fuel consumption of modern diesel generators also makes them a good choice for facilities that experience frequent or prolonged outages, as they do not require as much fuel to run for extended periods compared to natural gas-powered generators or battery backup systems.
Additionally, because diesel fuel is relatively easy to store and is readily available in many regions, maintenance and fuel logistics are simpler compared to more complex energy systems, contributing to overall cost savings.
Scalability and Flexibility
Diesel generators come in a wide range of sizes and configurations, making them adaptable to different power requirements. Whether a small facility needs a single generator to back up its operations or a large hospital complex requires multiple units to ensure full redundancy, diesel generators offer the flexibility to scale up or down based on the specific needs of the facility.
For example, a modular diesel generator system can be designed to provide backup power to a data center, with multiple units that can be switched on and off as necessary to match the load. This allows for dynamic power management during an outage, optimizing fuel use and ensuring that power is available when and where it is needed most.
This scalability and flexibility make diesel generators the go-to choice for a variety of critical infrastructure sectors, from military bases to transportation networks, where operational needs vary and must be met efficiently and reliably.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards
In many regions, critical infrastructure such as hospitals and emergency facilities are required to maintain certain regulatory standards regarding power backup systems. For instance, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) mandates that hospitals must have backup power that can supply emergency power to life-support systems for a minimum of 72 hours in case of a power outage. Diesel generators are designed to meet these stringent standards, offering the necessary power to ensure that life-saving operations are not interrupted.
Telecommunication facilities are also required to have backup power to ensure that emergency services, such as 911 systems, can continue to function. Diesel generators offer the reliability needed to meet these requirements, keeping critical communication systems operational when the power grid fails.
Environmental Impact and Innovation
While diesel generators are known for their efficiency and reliability, they have also been criticized for their environmental impact due to carbon emissions. However, modern diesel generators are increasingly being designed to meet strict environmental standards, reducing the amount of NOx (nitrogen oxides), CO2, and particulate matter emitted during operation.
In fact, advanced technologies such as clean diesel and hybrid generator systems are reducing the environmental footprint of these machines. Hybrid systems combine diesel with solar or battery storage to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and increase the overall energy efficiency of the system.
For organizations looking to minimize their environmental impact, diesel generators can be integrated into a broader energy strategy that includes renewable power sources, creating a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to backup power.
Backup Power in Emergency Situations
In emergency scenarios, where the local grid may be down due to natural disasters, power outages, or other unforeseen events, diesel generators provide critical backup power for disaster recovery operations. In areas prone to hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, having a reliable backup power source like a diesel generator can mean the difference between a facility being able to function and it being forced to close.
Disaster response centers, hospitals, and community relief hubs often rely on diesel generators to maintain power and continue providing vital services during emergencies. The ability to quickly deploy these generators into areas affected by disasters helps ensure that the response efforts continue without delay.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى