How Industrial Diesel Generators Are Enhancing Energy Security in Remote Areas
Dec 24, 2025
Content
Energy security is a critical issue for both developed and developing regions, especially in remote or off-grid areas where access to reliable and continuous power is limited. In many of these areas, energy infrastructure is either lacking or unreliable, making it difficult to meet the power demands of communities, businesses, and essential services. As the world continues to rely on electricity for virtually every aspect of modern life, ensuring a stable energy supply is vital for economic growth, public safety, and overall well-being.
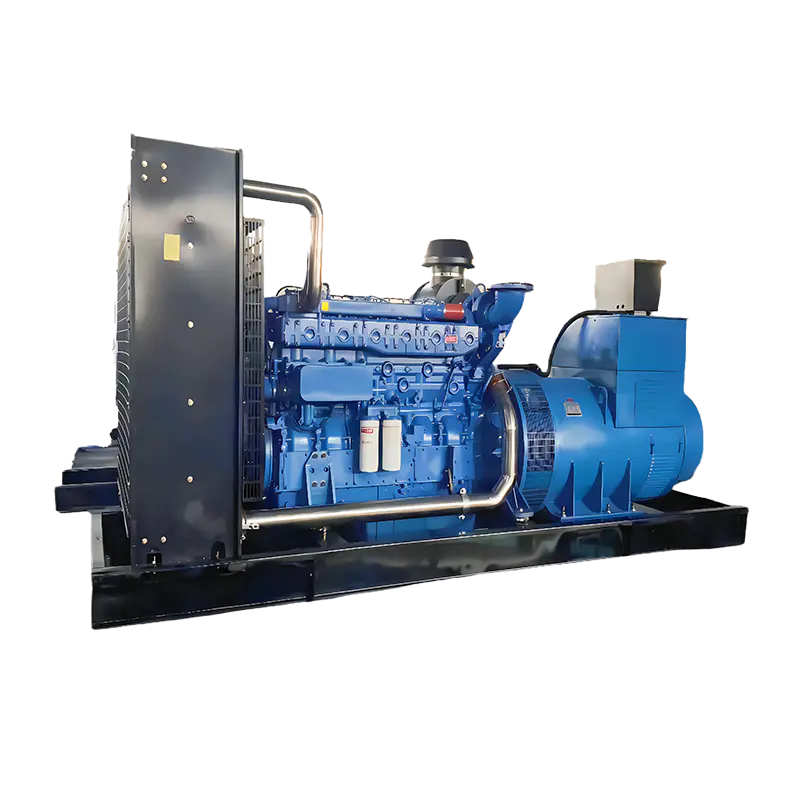
One of the key solutions to energy challenges in remote areas is the use of industrial diesel generators. These generators have become a lifeline for many remote communities, offering a reliable, cost-effective, and flexible source of power when the grid is either unavailable or insufficient.
The Importance of Energy Security in Remote Areas
Energy security refers to the ability of a region or country to access a reliable, affordable, and sustainable supply of energy. For remote or off-grid areas, energy security can be particularly challenging. Many of these regions are located far from national grids, and extending electrical infrastructure to these areas can be expensive, logistically challenging, and often impractical.
Without access to reliable electricity, communities in remote areas face numerous challenges:
- Limited access to healthcare: Without electricity, clinics and hospitals may struggle to power life-saving medical equipment, refrigeration for medicines, and basic lighting for patient care.
- Economic limitations: Small businesses, factories, and farms in remote areas depend on electricity for production, lighting, and tools. Lack of reliable power hampers their growth and sustainability.
- Educational challenges: Schools in off-grid areas may not be able to provide students with modern resources such as computers, internet access, or proper lighting for evening studies.
- Social difficulties: Lack of power affects social infrastructure, including community centers and communication networks, making it harder for people to stay connected and informed.
Given these challenges, energy security is essential to improving the quality of life and enabling sustainable development in remote areas. Industrial diesel generators are one of the most widely used solutions in such scenarios, providing a reliable source of power where other options may not be feasible.
How Industrial Diesel Generators Enhance Energy Security
Industrial diesel generators have long been recognized for their ability to provide reliable, efficient, and flexible power solutions, especially in areas that are not connected to national or regional power grids. Their contribution to energy security in remote areas is significant, offering several advantages:
Reliable Power Supply in Off-Grid Locations
One of the primary benefits of industrial diesel generators is their ability to supply power in areas that are disconnected from the grid. Unlike renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, which depend on environmental conditions, diesel generators provide a continuous power supply, irrespective of weather or time of day.
For remote communities, businesses, and industries that rely on consistent power, industrial diesel generators ensure that operations can continue without interruption. These generators can support a wide range of applications, from small rural clinics and schools to large mining operations or agriculture projects.
Scalability and Flexibility
Industrial diesel generators come in a wide range of sizes, from small portable units to large, high-capacity generators that can support entire villages or industrial operations. This scalability makes diesel generators particularly suitable for remote areas with varying power needs.
For example, small-scale operations like remote tourist lodges or agricultural farms can rely on smaller, more affordable diesel generators, while larger industrial sites such as mining companies or oil extraction facilities can use larger, high-capacity generators. This flexibility ensures that all types of energy needs are met, regardless of the specific scale or demands of the community or business.
Low Initial Investment and Fast Deployment
Compared to other energy solutions such as grid extension or renewable energy systems, industrial diesel generators offer a relatively low initial investment. Installing a power grid in remote areas can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming, especially in regions with difficult terrain or sparse populations.
In contrast, industrial diesel generators can be deployed quickly, providing immediate relief to areas in need of power. Their installation process is straightforward, and the fuel infrastructure for diesel generators is already in place in most regions. This makes them an attractive option for quickly improving energy security in remote communities without waiting for extensive infrastructure projects to be completed.
Energy Independence
One of the critical advantages of industrial diesel generators is their ability to provide energy independence. In regions that are dependent on an unreliable national grid, frequent power outages and disruptions can be common, especially during natural disasters or extreme weather conditions. Diesel generators allow communities to become less dependent on external power sources, reducing their vulnerability to grid failures and external factors that may disrupt electricity supply.
By providing on-site, independent power generation, industrial diesel generators enable remote areas to maintain essential services, economic activities, and social infrastructure even during power outages or other disruptions to the main grid.
Cost-Effective for Remote Operations
For many remote communities or businesses, the high cost of extending power lines or investing in renewable energy systems can be a significant barrier to securing reliable energy. Industrial diesel generators offer a more cost-effective solution, especially in regions where grid extension is not practical.
Although diesel fuel costs can fluctuate, diesel generators still remain a more affordable option compared to other energy solutions such as off-grid solar or wind installations, especially for communities with immediate or temporary power needs. Additionally, because diesel generators are widely available and relatively easy to maintain, ongoing operating costs remain manageable.
Support for Emergency and Backup Power
In remote areas prone to natural disasters, industrial diesel generators play a crucial role in providing backup power during emergencies. Whether due to storms, floods, or earthquakes, power outages are common in areas with vulnerable infrastructure. Diesel generators provide reliable backup power to critical services such as hospitals, emergency response centers, water treatment plants, and communication networks.
Having access to a reliable backup power source ensures that essential services continue to operate during emergencies, helping save lives, maintain communication, and facilitate recovery efforts.
Benefits of Diesel Generators in Specific Remote Areas
Industrial diesel generators support energy security in a variety of remote environments, each with unique challenges. Some specific benefits of diesel generators in different contexts include:
Remote Healthcare Facilities
In healthcare facilities such as hospitals or clinics, particularly in rural or remote regions, reliable power is essential for running medical equipment, refrigeration for medications, and providing lighting and cooling. Industrial diesel generators ensure that these facilities remain operational, even in the event of a grid failure.
For example, mobile healthcare units or rural health centers can rely on diesel generators to maintain critical services, especially when they are situated far from urban centers with stable electricity supplies.
Agricultural Operations
In agricultural communities, industrial diesel generators are often used to power irrigation systems, cold storage units, and machinery. Reliable electricity ensures that crops are watered and harvested efficiently, storage conditions are maintained, and food production processes run smoothly. Diesel generators are also used to power large farming equipment, ensuring that the agriculture sector operates efficiently even in remote areas.
Mining and Oil Extraction
In remote mining and oil extraction operations, industrial diesel generators are often the primary source of power. These industries are typically located far from national grids, and the demand for energy is significant. Diesel generators provide a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective solution for powering extraction equipment, lighting, communication systems, and essential support infrastructure.
Remote Communities and Villages
For small villages or remote communities with limited infrastructure, industrial diesel generators provide a vital source of power for lighting, heating, cooking, and running small businesses. They also enable access to modern conveniences such as refrigeration, internet, and communication systems, which are vital for improving quality of life and encouraging local development.
Environmental Considerations and the Role of Cleaner Technologies
While industrial diesel generators play a critical role in providing energy security, it is important to acknowledge the environmental concerns associated with their use. Diesel fuel is a fossil fuel, and its combustion releases greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere. As such, there is increasing emphasis on improving the environmental footprint of diesel power generation.
One of the key trends in industrial diesel generator technology is the development of cleaner, more efficient diesel engines. Advances in engine technology, such as lower emissions and improved fuel efficiency, are helping to reduce the environmental impact of diesel generators. Additionally, hybrid solutions that combine diesel generators with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, are becoming more popular in remote areas, further enhancing sustainability.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى